Text embedding with decoder-based Transformer
When we want to do text embedding, encoder-based Transformer such as BERT used to be the optimal choice. These encoder-based models are trained with bi-directional information which means that the embedding of each token considers the information of the whole sentence. On the other hand, the decoder-only models are trained with the causal mask which means that the tokens’ embedding only considers the information prior to them which make only the embedding of the last token has the information of the whole sentence. Therefore, using encoder-based models make more sense for the tasks using sentence text embedding.
However, the decoder-based Transformer is the backbone of the LLM and these LLM models are trained with huge amount of data and have shown promising results on various of tasks. Therefore, how to leverage these pre-trained LLM models to generate text embedding has been a new line of works.
Advantages of decoder-based transformer
- With the recent development of LLM community, we already have many powerful pre-trained models to start with
- These decoder-based LLMs have been developed to be good at instruction following and therefore could generalize over a variety of tasks with instructions
- Since encoder-based Transformer rely on masking around 15% of tokens during training while it is not the case for the decoder-based model, given the same training data size the decoder-based model is more efficient to learn all the tokens.
On the other hand, the disadvantage of the decoder-based transformer is also obvious which is they rely on causal masking and the masking does not make sense for the text embedding tasks and therefore in this line of papers the authors all removed the constraints.
LLM2Vec
In the LLM2Vec paper, the figure 1 summarizes how they approach the problem.
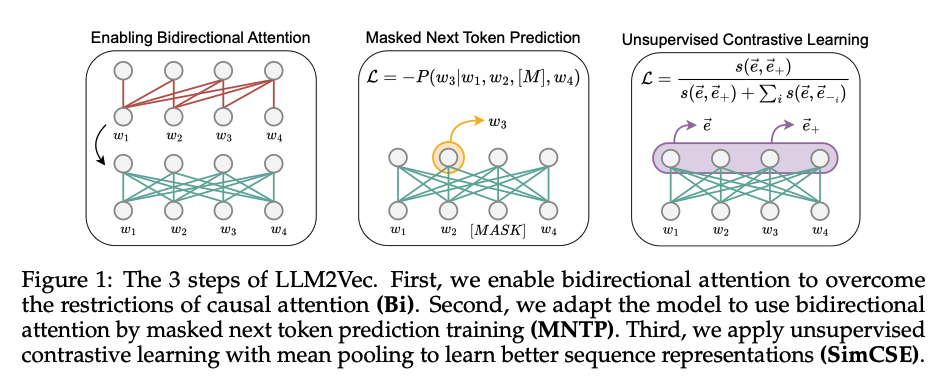
The very first step is enabling the bidirectional attention. In this way the embedding is obtained with all information of the input sentence.
The second step is training the model with the masked next token prediction to make the model aware of the bidirectional attention enablement. The paper used LoRA to fine tune the base model, and therefore we would have an adapter after the training.
With the above two steps, we should have a model that could leverage the whole sentence information to generate the corresponding token embedding. However, we need the model to give us the sentence/document embedding. Therefore, the third step is using unsupervised contrastive learning via SimCSE to help the model learn the sequence embedding. In the contrastive learning, the dataset is composed as below
- Positive pair: Send the input text to the model twice and with the dropout mechanism we would have two sequence embedding. They would be positive pairs
- Negative pair: Sequence embedding from different input pairs
Pooling
The paper tried three types of pooling approach: EOS, mean pooling and weighted mean pooling. The authors found that the mean pooling approach worked the best overall. How the pooling approaches are implemented is shown through the code here. As a side note, the weighted mean pooling here means the tokens in the later part of the sequence would have larger weights.
LLM2Vec with supervised training
The LLM2Vec could be combined with the supervised learning. In the paper the author used contrastive learning with the labeled dataset. (Like information retrieval dataset.) The training combined the instructions listed in the Table 10 to generate the embedding. How the training works is like the one described in the other paper. Given a relevant query-document pair, we have
\[q^{+}_{inst} = \textrm{Instruct:}\{\textrm{instruction}\} \setminus n \textrm{Query}\{q^{+}\}\]With the above and the document embedding, we could apply the InfoNCE to train the model.
Implementation details of bidirectional attention
From the huggingface repositoryMcGill-NLP/LLM2Vec-Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct-mntp, we see that it defines a class LlamaEncoderModel (here). In this class, every layer now is a ModifiedLlamaDecoderLayer which turned off all the is_causal flags.
However, how the code and model are loaded through the huggingface config along with the base model is another topic.
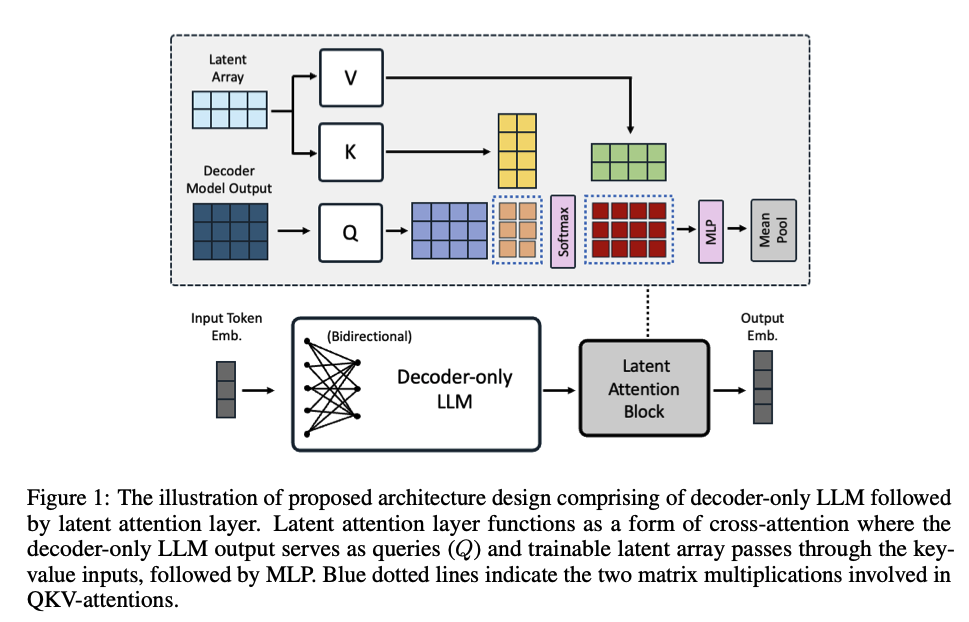
NV-Embed and latent attention layer
The other paper NV-Embed is also utilizing LLM for text embedding. In this paper the backbone idea is the same which is removing the causal attention mask. The interesting idea of the paper is the authors proposed using latent attention layer instead of pooling for generating the final sequence embedding. From the authors’ statement, different types of pooling have their own limitation
- Pooling with
token: It would suffer from recency bias - Mean pooling: Dilute the important information from key phrases
How latent attention layer works is as the below figure: